
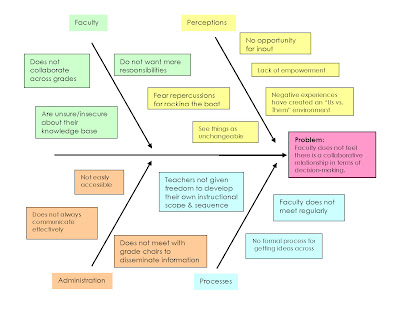
List the major categories for potential causes.
Cause and effect charts full#
Include elements such as who, what, when, where, and how much in the full problem statement. Include a title or summary in the box on the diagram, yet capture the complete problem statement elsewhere. the box with the problem statement is to the right (taking advantage of time progress to reinforce the causes, which occur before the problem occurs). Start with a basic fishbone diagram as above.Steps to Create a Cause and Effect Diagram This tool really only focuses on one question: What is a cause of this problem? Engineers seem to be ready to solve symptoms without first understanding the root causes. Focuses the team on causes and not symptoms.It not only captures all the possible causes it also organizes them into categories and subcategories. The diagram captures the current thinking around a problem.At first, the ideas flush out the categories and may include secondary (or more) branches from the initial ideas along a similar line of reasoning. This process is inherently visual and uses a simple branching structure to quickly organize potential causes. This helps you and the team think about the range of different potential causes of the problem. The fishbone diagram starts with categories of potential causes. One issue with any brainstorming process is the early ideas become a focal point for future ideas. There are four significant benefits to using a fishbone diagram with a team, or even on your own. The Ishikawa diagram is one of the seven basic tools of quality control.
Similar to a brainstorm session about the problem, this graphical tool provides a bit of structure and may prompt additional potential causes. This diagram is part of a complex failure analysis process when there are many potential causes for the problem or condition. The intent is to expose the most likely root causes for further investigation. Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process courseĪlso called the Ishikawa or fishbone diagram, the cause and effect diagram is a graphical tool that enables a team to identify, categorize, and examine possible causes related to an issue.Reliability Engineering for Heavy Industry.An Introduction to Reliability Engineering.Reliability Analysis Methods online course.14 Ways to Acquire Reliability Engineering Knowledge.Innovative Thinking in Reliability and Durability.Equipment Risk and Reliability in Downhole Applications.Musings on Reliability and Maintenance Topics.Metals Engineering and Product Reliability.Asset Management in the Mining Industry.Product Development and Process Improvement.Rooted in Reliability: The Plant Performance Podcast.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
